Here’s a breakdown of the average energy bill to give you a better idea of where your money is going.
Here’s a breakdown of the average energy bill to give you a better idea of where your money is going.
Your gas and electricity utility bill sets out the charges you’ve incurred as a gas and electricity customer.
Your energy supplier sends you your utility bills on a monthly or quarterly basis so that you can understand how much you owe.
The average utility bill is made up of several different components, with the majority of your payment going on the energy you use.
But there are other costs factored in, like distribution charges, environmental costs and VAT.
Here’s how the average energy bill breaks down to give you a better idea of where your money is going.
Breakdown of the average energy bill
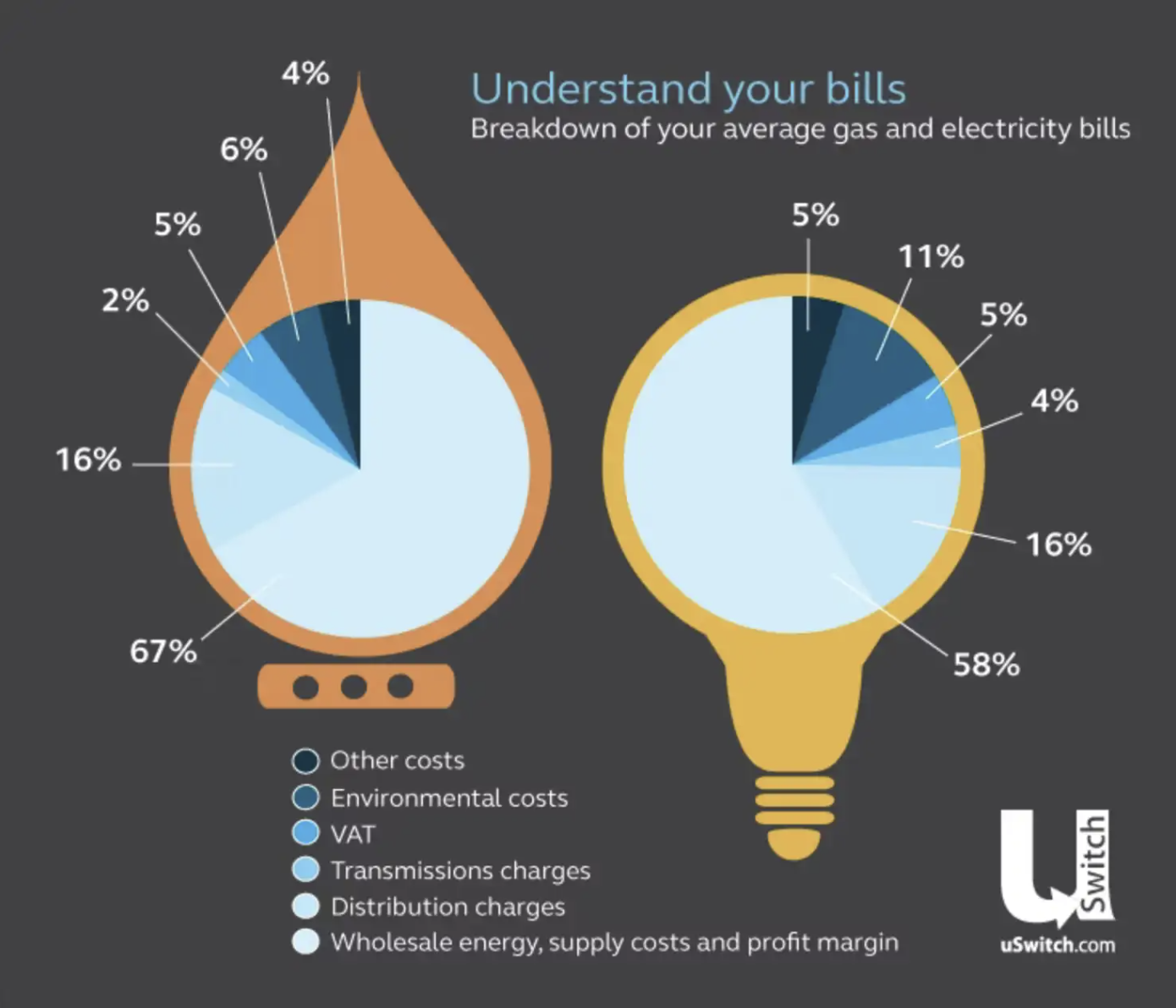
Where your gas payment goes
-
67% on wholesale energy, supply costs and profit margin
-
16% on distribution charges
-
6% on environmental costs
-
5% on VAT
-
4% on other costs
-
2% on transmission charges
Where your electricity payment goes
-
58% on wholesale energy, supply costs and profit margin
-
16% on distribution charges
-
11% on environmental costs
-
5% on VAT
-
5% on other costs
-
4% on transmission charges
Environmental costs
A proportion of your gas and electricity bill is used to subsidise the government’s environmental initiatives.
Environmental costs comprise approximately 6% of your gas bill and 11% of your electricity bill.
Environmental schemes which are subsidised by your gas and electricity bill include:
-
Feed-in Tariff scheme (FITs)
-
Carbon Emissions Reduction Target (CERT)
-
Community Energy Saving Programme (CESP)
-
The Renewables Obligation (RO)
-
EU Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS)
Find out more about the Feed-in Tariff scheme on Uswitch.
VAT charges
Contrary to popular belief, you do not pay full VAT on gas and electricity, but you do pay some.
Currently, VAT payments are capped at 5% of your total bill.
Transmission charges
Transmission networks are what actually deliver electricity and gas to your home, and some of the cost of building and maintaining transmission chargers is passed on to customers.
Currently, 2% of your gas bill and 4% of your electricity bill make up these costs.
Distribution charges
16% of your gas bill and 16% of your electricity bill go towards distribution costs.
This covers some of the cost of building, maintaining and operating the local gas pipes and electricity wires which deliver energy to the home.
Wholesale energy and supply costs
The bulk of your bill, unsurprisingly, is comprised of charges for the gas and electricity you actually use.
This comes to roughly 67% and 58% of your respective bills.
Wholesale cost is the price that the energy supplier has to pay for the gas and electricity they buy.
Supply costs are the costs the energy supplier incurs for the general administration associated with a retail business, like running a call centre and sending out bills. These vary according to which tariff you’re on.
Compare gas and electricity deals on Uswitch
Other costs
Other costs cover things like meter installation and gas storage, which comprise about 4% of your gas bill and 5% of your electricity bill.
How can you bring your energy bill down?
These energy-saving tips will help bring your energy bills down and reduce your carbon footprint.
Heating
The biggest portion of your energy bill is taken up with heating your home and water.
Follow these tips and you could save a fortune on your heating bills:
-
Turn your thermostat down by a single degree. This could save you as much as £60 on your energy bills over the space of a year.
-
Make sure your home is adequately insulated. Loft and cavity wall insulation may require an initial investment, but could easily save you hundreds a year in heating costs.
-
If you’re on a low income, you may be eligible for an energy efficiency grant to make improvements to your home.
-
Try to block any draughts that are coming into your house and make sure you close your curtains to keep the heat in.
In the kitchen
The next largest portion goes towards powering your washing machines, fridges, freezers and cooking appliances.
Keep kitchen costs down with these tips:
-
Do your washing less frequently. It may sound obvious but make sure the machine is full every time for maximum efficiency.
-
Use the economy setting on your washing machine. Many washing powders will now work at temperatures as low as 30 degrees, which is enough to effectively wash clothes while also helping your machine run more efficiently.
-
Dry your clothes outside or on a clothes horse. Tumble dryers use a lot of energy, so if you can dry your clothes for free, that will help keep costs down.
-
Replace your current fridge and/or freezer with an energy-efficient model. Look out for the energy efficiency stickers on modern appliances. You should also make sure they’re kept as full as possible and that the area around them is clean so they don’t have to work as hard.
Computers, gadgets and electronics
Next up is the amount of energy used by consumer electronics such as DVDs, TVs and computers every year.
Bring these costs down by:
-
Turning electronics off instead of leaving them on standby. If you’re forgetful, invest in a standby saver – it will automatically cut the power to any electronics left on standby.
-
Only charging devices when you need to. Don’t leave laptops and mobile phones charging overnight as this is a big waste of energy.
Lighting
Finally, there is the portion of bills going towards lighting your home.
The quickest and easiest ways to save on your lighting costs are to:
-
Buy energy-efficient LED lightbulbs. They last up to 24 times more than incandescent lightbulbs and each one you swap could save you at least £4 per year.
-
Turn the lights off behind you when you leave a room and get into the habit of switching the lights off as you move through the house.
